
Matt, USA
Matt is our Spaya expert. He has a background in Organic Chemistry and Medicinal Chemistry and is ready to help you solve any roadblocks.
Spaya is our advanced AI-powered retrosynthesis platform that rapidly transforms target compounds into commercially available starting materials. It enables real-time exploration of all plausible synthetic routes, accelerating your research and enhancing efficiency.
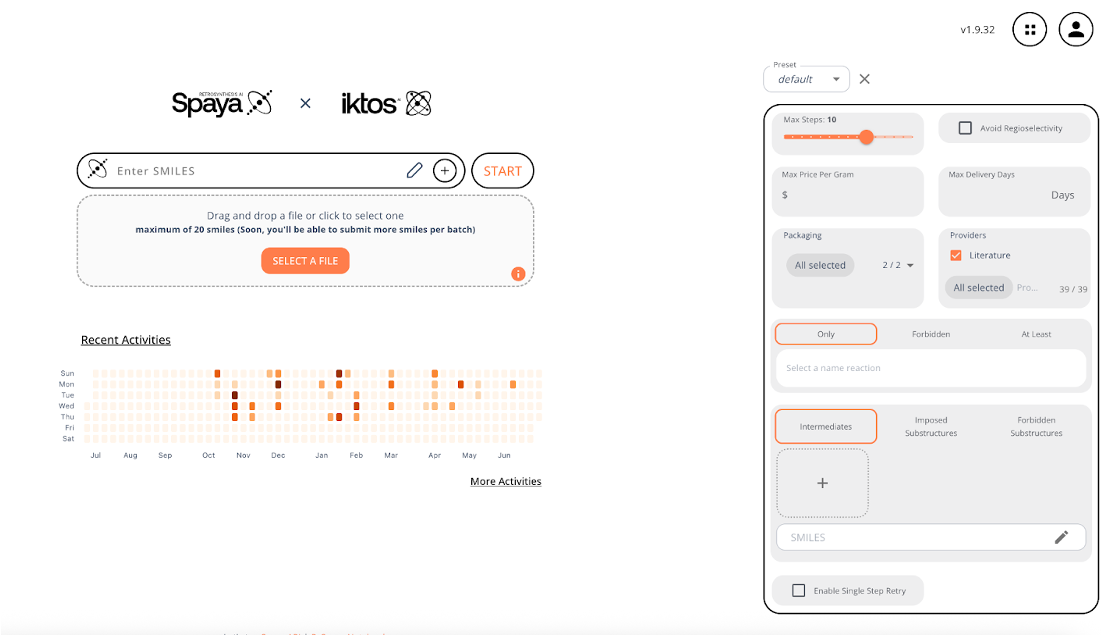
Interact with retrosynthetic routes in real time with the fastest solution on the market.
Quickly analyze results and organize targets based on RScore.
Quickly order starting material as all routes end in commercially available starting material by design

Learn how to customize a route to meet your project needs
Watch now - 1 min
Learn how to update settings with reaction types and commercially available building blocks
Watch now 1:30 min
Learn how to navigate Spaya's reaction trees effectively
Watch now - 1 min
Lear how to obtain routes for multiple compounds at the same time
Watch now - 1 min
Learn how to navigate results for batch searches
Watch now - 1 minThe RScore, or Retrosynthetic Score, is a composite score that ranks proposed synthetic routes by assessing each step’s likelihood based on context, penalizing longer sequences, and favoring similarity to literature precedents, route convergence, and model confidence—with scores ranging from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates an exact literature match. Generally, we recommend a threshold of >= 0.5.
Spaya uses a chiral pool approach to retain stereocenters from commercially available starting material. If Spaya cannot identify a chiral route, it is recommended to remove chirality from the initial structure.
If Spaya cannot identify a route, it is recommended to iteratively relax system constraints. In default mode, the number of steps is set to 10. First, adjust the number of steps to 15, then remove advanced parameters and/or chirality, before reinitiating retrosynthesis.
Occasionally, due to the difficulty in extracting patent information, Spaya may not provide precise conditions. It is recommended to review the patent in detail outside of Spaya, using the patent number provided.
Substructure searching identifies molecules containing a specific chemical fragment within a database, while retrosynthetic analysis breaks down a target molecule into simpler starting materials to plan a synthetic route.
Integrating synthetic accessibility with AI-based generative drug design, Journal of Cheminformatics volume 15, Article number: 83 (2023).
Predicting the Price of Molecules Using Their Predicted Synthetic Pathways, Molecular Informatics, Volume44, February 2025.
In our sessions we will teach you how avoid common pitfalls and optimize retrosynthesis set-up, to get optimal results, fast.

Matt is our Spaya expert. He has a background in Organic Chemistry and Medicinal Chemistry and is ready to help you solve any roadblocks.
Yes! Spaya is data-driven and readily customizable. Reach out to our support team at support@spaya.ai to learn more about how to retrain Spaya on your ELNs, additional reaction data sources, or to add proprietary building blocks and vendors.
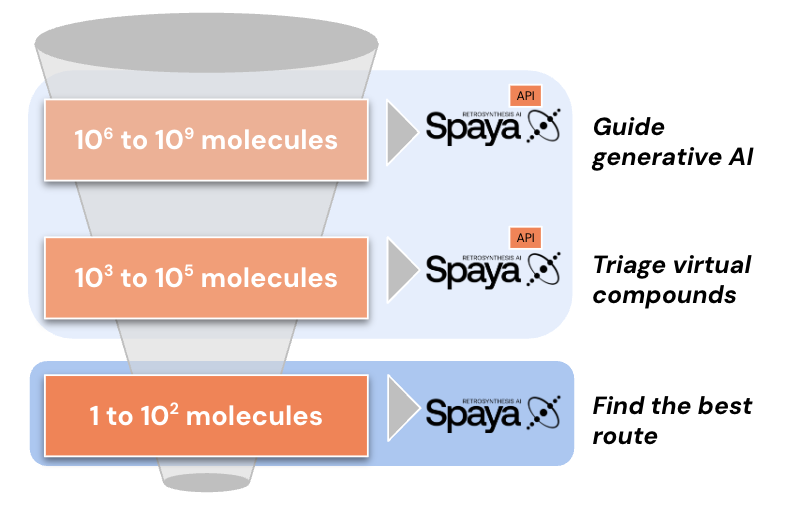
Spaya has a programatic interface known as Spaya API that can be integrated into your internal workflows using platforms like Knime, Pipeline Pilot, Jupyter Notebook, and more. Available on AWS with autoscaling or on your VPC. All advanced search parameters available within the GUI are also applicable via the API. Reach out at support@spaya.ai to learn more!
The two key differences between the Spaya GUI and API are interface and scalability. All advanced search parameters available in the GUI can also be accessed programmatically through the API. However, the Spaya API supports scaling to thousands of retrosynthesis, whereas the GUI currently allows batching of up to twenty targets at a time.
It is possible to run a batch retrosynthesis on Spaya GUI. Note that this feature will only call up to 20 retrosyntheses at a time. In order to scale beyond this, you will need access to Spaya API. Spaya API is a programatic interface that rapidly returns full retrosynthetic analysis for up to hundreds of thousands of molecules.